The escalating tensions, world food shortage, and financial crises had a destabilizing influence on the European security and the global energy market, followed by the food market. The protracted conflict in Ukraine could raise food prices around the world - and hit countries that already have food problems the hardest.
In this article, we will reveal our thoughts on the global crisis, food shortage, and its impact on the tech world. The world economy is changing: the stock market is collapsing, the crypt is falling sharply, the IT bubble is bursting, and there is a fuel crisis and the threat of global hunger. What awaits the planet's economy next?
What is Food Crisis?
The food crisis is a term used to describe a situation where countries or people do not meet their food needs. The food crisis can have several stages. For example, it can occur due to:
- a shortage of products
- complete hunger
- conflict
- poverty
- economic shocks such as hyperinflation
- environmental shocks such as flooding or drought
- rising food and commodity prices resulting in a financial crisis and the growing global food crisis.
There are several factors that directly or indirectly affect the increase or rise in food prices around the world that cause the food crisis, among which are the following:
- Owners of capital finance agricultural raw materials and food, which directly and proportionally affects the cost of raw materials and finished products.
- Much of the production of soybeans, wheat, corn, and rice is diverted to biofuel production. It leads to an increase in the cost of raw materials and the final product. Today, there is a decline in agricultural productivity, as governments and large companies prefer to produce goods that serve biofuel companies, as this is more profitable than food production.
- The drastic changes in climate that have damaged plantations and crops, and therefore the production of food materials, are declining.
Forty-five million people are experiencing starvation in the world right now with children and women hit the hardest. Approximately 584,000 people face catastrophic levels of hunger, and it has rapidly increased in the past six months.
The war in Ukraine has caused a global food crisis that could last for years. The war cut off supplies from Ukrainian ports, which once exported large quantities of oil and grain such as corn and wheat. It has reduced global supply and led to a sharp rise in prices for alternatives. According to the UN, world food prices are almost 30% higher than at the same time last year.
Some Ukrainian elevators are located in the territories temporarily occupied by Russia. The Russians steal this grain, export it to Crimea, and export it as Russian. The occupiers have already sent approximately 400-500 thousand tons of grain to the Crimea. Given that a ton costs $250-300, the losses of Ukrainian farmers are at least $125 million.
Meanwhile, one of the world's largest grain producers, India, banned wheat exports. The country's authorities took this measure, seeking to provide food for their own population. Another 11 countries have already followed India's example by banning the export of grain, sunflower and palm oil, and fertilizers.
Experts say the war could raise food prices and increase the threat of global hunger.
How the war in Ukraine affects the whole World
With 855 million people already suffering from food insecurity, Russia's invasion of Ukraine came at a difficult time for global hunger. Disruption in food production increases the risk of hunger among Ukrainians. However, given the enormous role of Russia and Ukraine in providing the world with food, including wheat, instability in food production and exports could have consequences that go far beyond the war territory.
The number of starving people in the world has grown over the past five years. The main reason is rising food prices. Due to the war in Ukraine, the increase in hunger strikes this year will be from 20 to 50 million people. World grain prices have risen by more than 50% since the beginning of the year.
The war in Ukraine threatens the global crisis. Dozens of countries in the Middle East, South Asia, and North Africa that are already suffering from food shortages are relying on supplies from Russia and Ukraine (Egypt, Yemen, Israel, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Ethiopia, Libya, Lebanon, Tunisia, Morocco, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Turkey). These countries are the primary buyers of wheat and corn on world markets.
- Due to the war in Ukraine, grain prices in the world increased. The fighting has already led to indirect pressure on world grain prices. Russia continues to block Ukrainian ports, leading to a shortage of supplies and further rising prices for many essential products.
- Before the war, Ukraine supplied 10% of world exports of wheat, more than 15-20% of barley, and more than 50% of sunflower oil. Ukraine has limited exports during the war.
- Russia and Ukraine account for 28% of world wheat exports. If Russia restricts sales, it will not hit Western countries directly because they don’t buy much Russian grain. Developing countries will feel the consequences. And the poorer the state, the stronger the effects of rising prices for it.
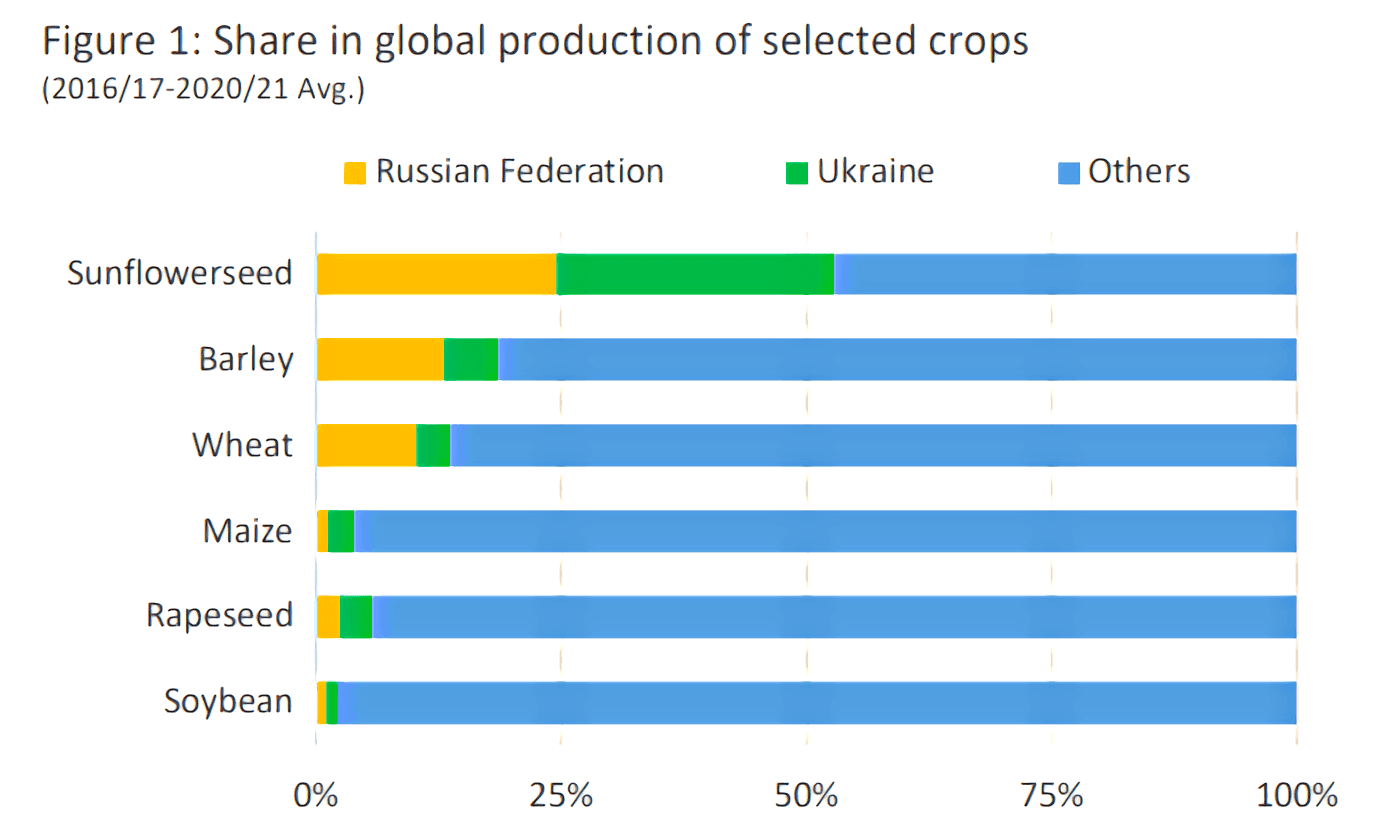
Now the world's most developed countries are trying to anticipate and prevent a possible food crisis. The G7 countries have allied to ensure global food security. The newly created structure organizes the financing and cooperation of states in providing the world's population with food.
Food, Energy, and Finance Crisis — a real threat to Global Economics?
In 2022, the world was waiting for economic recovery, but the Russian military invasion of Ukraine shattered all hopes for a stable life.
Protecting the vital interests of the citizen, in particular, unimpeded access to food is a guaranteed priority for any country in the world. Ukraine, like other civilized countries of the world, at its national level, creates all the conditions to ensure the needs of the population with food availability, quality and safety of products, and free access to natural resources.
The UN fears that the food crisis could worsen if countries respond to it by closing food markets. It will create a domino effect of export bans, threatening catastrophic consequences.
Another factor of instability may be the shortage of energy, which will affect the cost of utilities and the work of several industries.
The global economy is likely to slow down. Of course, this will be felt differently in different regions of the world: in the United States and Europe - to a lesser extent, but the crisis will hit much harder in Africa and the Middle East. The main areas that experience changes are:
In 2022, the world was waiting for economic recovery, but the Russian military invasion of Ukraine shattered all hopes for a stable life.
Protecting the vital interests of the citizen, in particular, unimpeded access to food is a guaranteed priority for any country in the world. Ukraine, like other civilized countries of the world, at its national level, creates all the conditions to ensure the needs of the population with food availability, quality and safety of products, and free access to natural resources.
The UN fears that the food crisis could worsen if countries respond to it by closing food markets. It will create a domino effect of export bans, threatening catastrophic consequences.
Another factor of instability may be the shortage of energy, which will affect the cost of utilities and the work of several industries.
The global economy is likely to slow down. Of course, this will be felt differently in different regions of the world: in the United States and Europe - to a lesser extent, but the crisis will hit much harder in Africa and the Middle East. The main areas that experience changes are:
- Food and energy prices will rise. Ukraine, which is suffering from the war, and Russia, whose economy is adapting to living under sanctions, are the world's largest raw materials suppliers. Thus, disruptions in production and supply will lead to a rise in world prices, especially for oil and natural gas. It means that we can continue to expect rising inflation and impoverishment.
- Europe is already watching the unprecedented flows of migrants, who also need financial support. The UN estimates that more than 3 million Ukrainians are already fleeing the war abroad. European countries may also face significant increases in defense and energy security expenditures.
- There will be more uncertainty for business, an unfavorable investment climate, and an outflow of capital from promising markets.
- The war in Ukraine has pushed oil, gas, and electricity prices up tens of percent. However, the black gold and blue fuel are still one and a half times more expensive than at the beginning of 2022. The UN is worried that high prices may influence the investments in fossil fuels and reverse the progress of the last 5-10 years towards decarbonization.
- Another loss of the war is the production of neon, a relatively rare gas, more than half of which was produced at Ukrainian enterprises in Mariupol and Odesa. Now Ukraine cannot meet world demand. The manufacturers need neon to make chips - they go to the creation of medical equipment, computers, and smartphones. It may take nine months to two years to establish production in other countries.
- The price of coal is also at its peak - $400 per ton. It is four times more than in the same period of 2021. Rising coal prices will hit economies dependent on this fuel hard.
The war in Ukraine affected other industries as well. According to the Financial Times, BMW and Volkswagen are forced to shut down plants across Europe due to a lack of car wires manufactured at Ukrainian plants. Ukraine accounts for almost a fifth of all European imports of car wires, and it is impossible even partially to start assembling the car without them.
Supply and demand shocks have already led to record price increases. It could lead to stagflation in the future. Stagflation is the state of the economy when prices rise, and jobs and wages fall. This combination of stagnation and inflation can lead to a protracted crisis.
The Burst of a Crypto Bubble
The US stock market and the world is experiencing unprecedented shock: by early May, the index of leading US stocks S&P 500, fell by 18% from a record high in January. The NASDAQ index, the over-the-counter securities market of high-tech companies in the US, Canada, Israel, etc., has fallen by 29% since November. According to The Wall Street Journal, all of this results from significant market turbulence caused by inflation in the United States.
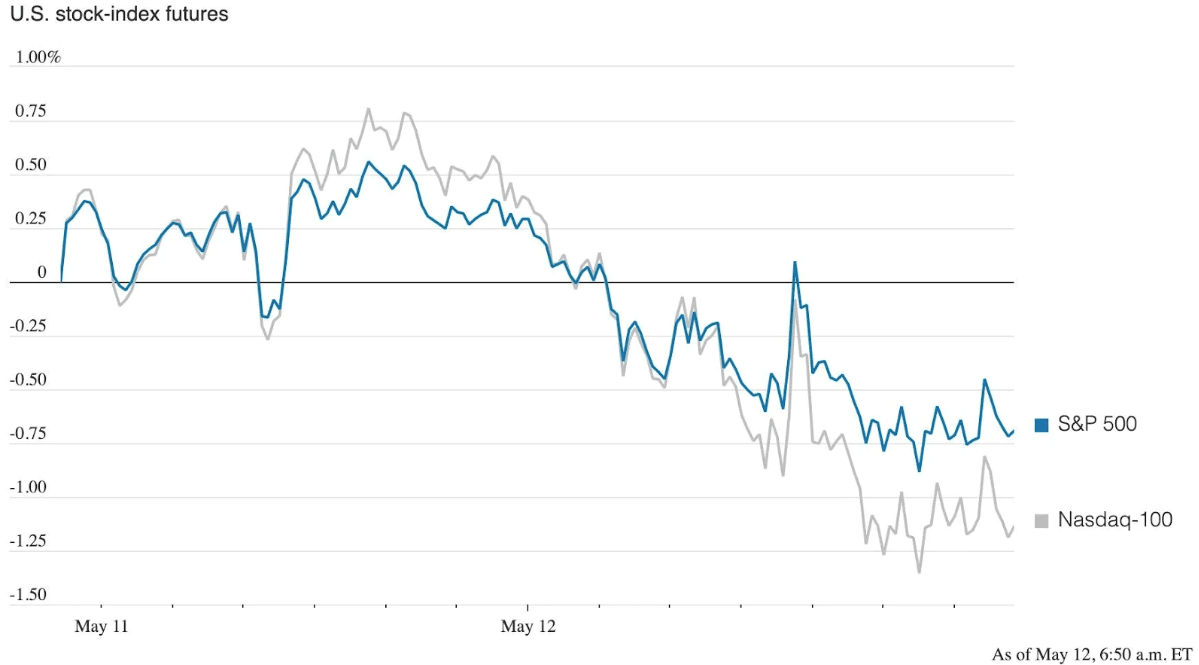
The higher the inflation, the more aggressively the central banks have to act. Elevated accurate interest rates destroy the present value of future cash flows. It has led to a massive sell-off of high-tech stocks based on expectations of much higher returns in the future. For the same reason, prices for long-term bonds fell sharply.
Following reports that the US Federal Reserve aims to regulate monetary policy, there were first rumors that the most popular cryptocurrency may fall. Despite the expected sudden collapse, the loss of value was relatively gradual. The rate was continuously declining. The US Federal Reserve has raised interest rates by 50 basis points, the most significant increase in more than 20 years. The central banks of other countries did the same.
Cryptocurrencies are seen as risky assets, and when markets are uncertain, institutional investors sell them and invest in safer investments. It is the reason for the fall in the rate of bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
Bitcoin is trading at around $31,420 today, twice as low as in November 2021. Ether (Etherium) fell 10.1% to $1911 in early June - the lowest level since July 2021. Previously we had the big UST crash in May. The Terra UST "stable coin" has broken away from $1 recently, reaching 34 cents, dragging down the whole ecosystem. Its subsidiary token Luna traded for 15 cents, 97% less than previous days. The Terra Blockchain officially halted for the first time, bringing uncertainty around the whole Crypto world. The Blockchain halted again, which resulted in dramatic Luna crash to $0,00018, which is peanuts compared to $119 All-time-high. Do Kwon, the owner of Terra Network, announced the Terra 2.0 and renamed UST to USTC (Classic) and LUNC. However, new LUNA and UST didn't help much, burning down the investor's portfolios and fueling the market to go bearish even more.
The NFT boom has probably also passed: if in September last year, NFT sales reached 225,000 per day, in the last week of May, the average was barely 19,000.
According to analysts, digital assets are increasingly moving in step with stocks, as traditional hedge funds have been actively entering cyberspace over the past two years. Such funds are more likely to dump cryptocurrency assets during periods of volatility than to hold them.
Despite all the difficulties, the Ukrainian IT industry provided a record $ 2 billion in export revenues for the 1st quarter of 2022. This figure increased by 28% compared to last year, despite the war and relocating employees and companies.
Changes to the Job Market
The Ukrainian and world labor markets will no longer be the same as before. If we used to depend on the external situation directly, today, the war in Ukraine changed the previous paradigms and principles according to which both the economy and the labor market function.
- More than 20% of the Ukrainian population has left their homes. More than 5.6 million citizens have gone abroad, and it is expected that about 2 million citizens will not come back in the coming years, even after the war. Another 8 million are internally displaced persons.
- Inflation expectations show that inflation will be more than 16% in the best scenarios.
- 80% of exports are blocked due to the closed sea routes and access to ports, complicated transport connections, limited rails with the EU, and lack of transit through Russia and Belarus. It means that export-oriented enterprises will be forced to reduce production.
Under these circumstances, the employers plan to revise their personnel policies. About 74% of companies plan staff changes. Among the top 5 measures are freezing budgets for training (26%), abolishing bonuses (16%), reducing staff (13%), reducing salaries (11%), and discharging employees (2%).
Another alarming situation is the US labor market, dominated by steady employment growth. It could lead to rising wages and inflation, forcing the Federal Reserve to take additional measures that could further scare institutional investors.
The problem for the state, the economy, and the citizens is that it will be challenging to quickly restore the pre-war level of employment. In addition to the physical destruction of enterprises and the loss of jobs, several other factors will hinder the rapid resuscitation of the labor market.
Digitalization and automation of processes in the world also significantly impact the labor market. The quality and productivity of labor are increasing, as well as the qualified specialists with the necessary skills. Some professions are losing demand. Further digitalization and the introduction of innovations in the work processes of companies in various industries guarantee the growth rate of the IT sphere.
According to some predictions, the information technology industry will grow by 22% by the end of this decade. Demand for programmers, which has been relatively high in recent years, will also increase. The most popular professions will be developers, DevOps engineers, analysts, and software testers. Increased demand for specialists will lead to a further increase in salaries in the IT sphere.
Conclusion
There is no catastrophe in the world economy yet, although consumption may soon begin to slow down. However, the war remains an important factor, and the only way out of the crisis is Russia's military defeat. The main priorities around the world will change. Let’s see how.
- Security
The war in Ukraine will radically change the global agenda and the concept of sustainable development (which is based on responsible environmental consumption and production). - From Global to Local
It will lead to a new stage of localization, where more and more industries will be located closer to the market. The result will be accelerated automation and population migration. - Energy safety
Alternative energy will get another boost. Moreover, it will have a positive effect on slowing down climate change. - Demand for the professional military
Demand for the military will increase, and military intelligence will be a priority. - Medicine
Treatment and rehabilitation of the past and unknown future challenges will make the demand for medical professionals sustainable. Increasing demand will increase wages and investment in medical infrastructure, education, and science. - Energy
There will be more development of alternative energy (biofuels, biogas, wind, hydro, solar), shale gas production, and investments in gas, oil, and coal production. - Microenterprise services for export
The opportunity to work remotely in the global market will cover every possible sphere.
We can also observe positive changes in the attempts and methods to solve the global crisis. An essential role in developing renewable energy is the "green tariffs" - a mechanism to stimulate investment in Green Energy through long-term contracts for the sale of electricity at a fixed price higher than the market. The advantages of the "green tariff" are not only in the higher price but also in the long-term contract, reducing investors' risks. Green tariffs are very effective in stimulating the rapid development of Green Energy but can be costly for governments. For example, the leading French state-owned company EDF Renewables expands renewable energy in more than 20 countries. It plans to double its global RES capacity from 28 GW to 50 GW in 2030.
The environmental sustainability of agriculture is also a matter of food security and the development of rural communities. More and more agricultural practices have become the basis for the green reconstruction of countries' agri-food systems. It is vital to switch to the small farmers with short production chains that adhere to agri-environmental principles. They can ensure food security and sustainable agricultural development in the local region and the world.
Also, more countries are investing in energy efficiency that brings more efficient solutions. The lower the energy consumption, the fewer households pay for utilities. In addition, investing in energy efficiency stimulates the economy, especially the construction industry, and creates jobs. After all, energy modernization projects of buildings create additional demand for construction products, equipment, and skilled workers.
The crisis is always followed by rapid growth, and our next article will be about possible directions after the crisis. You can check our other articles on our blog
If you experience any business challenges or don’t know where to start, we are always ready to help you. Let's talk and see how we can grow your business together and attract your customers.